High Costs and Affordability: Pharmaceutical companies often justify high drug prices due to the costs of research, development, and regulatory approval. This can lead to affordability issues, especially for life-saving medications.
Healthcare System Disparities: Disparities in healthcare systems across countries affect drug access. Developing countries may struggle to afford medications that are readily available in wealthier nations.
Intellectual Property and Patents: Patent protection allows pharmaceutical companies to recoup R&D costs but can restrict generic competition, keeping prices high. Balancing innovation incentives with affordability is crucial.
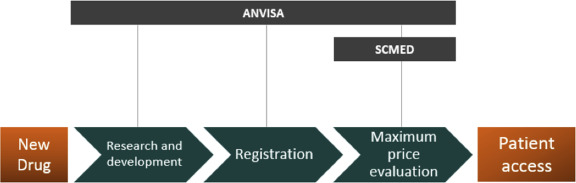
Regulatory Hurdles: Regulatory processes vary globally and can delay drug approvals, impacting timely access to new treatments. Stringent regulations ensure safety but may prolong access for patients.
Market Dynamics and Monopoly Pricing: Limited competition due to patents or market exclusivity can lead to monopoly pricing, where companies set prices without competitive pressures, exacerbating affordability challenges.
Insurance Coverage and Reimbursement: Insurance coverage varies widely, affecting affordability and access based on individual or national healthcare systems. High out-of-pocket costs can limit accessibility.
Ethical Concerns: Pricing decisions raise ethical questions about balancing profit motives with public health needs. Access to essential medicines is considered a human right, prompting debates on corporate responsibility.
Global Health Priorities: Diseases affecting low-income populations may receive less R&D investment, leading to fewer treatment options and higher prices for neglected diseases.
Health Technology Assessment (HTA): Assessing the value of new drugs relative to existing treatments is crucial for pricing decisions. HTA frameworks differ, influencing access and affordability across jurisdictions.
Patient Advocacy and Policy Efforts: Advocacy groups and policymakers push for reforms to address pricing transparency, affordability programs, and equitable access strategies, aiming to mitigate these challenges.
Biologics and Specialty Drugs: The rise of biologics and specialty drugs poses unique challenges due to their complex manufacturing processes and high costs. These medications often target rare diseases or specific patient populations, limiting economies of scale and affordability.
Price Negotiations and Transparency: Lack of transparency in drug pricing can obscure actual costs and inhibit effective negotiations between payers (such as insurance companies or governments) and pharmaceutical manufacturers. Transparent pricing mechanisms could potentially lower costs and improve access.
Impact of Health Crises: During health crises such as pandemics or outbreaks, rapid access to affordable treatments becomes critical. However, pricing pressures can escalate amid urgent demand, highlighting the need for coordinated global responses and pricing strategies.
Health Equity and Access Disparities: Vulnerable populations, including low-income individuals and marginalized communities, often face greater barriers to accessing essential medications due to financial constraints, geographic isolation, or systemic discrimination.
Drug Shortages: Shortages of essential medications can occur due to manufacturing issues, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory challenges. These shortages can lead to increased prices or limited access, impacting patient care and public health outcomes.
Political and Regulatory Environment: Changes in political leadership, healthcare policies, or regulatory frameworks can influence drug pricing dynamics. Uncertainty or shifts in policy can impact investment decisions by pharmaceutical companies and affect drug access.
Global Trade Agreements and Intellectual Property Rights: International trade agreements and intellectual property rights (IPRs) frameworks can affect drug pricing and access. Disputes over patents, compulsory licensing, and trade restrictions can impact affordability in different regions.
Healthcare Provider Practices: Prescribing patterns and formulary decisions by healthcare providers and institutions can influence the availability and affordability of medications for patients. Education and guidelines play a role in shaping these practices.
Patient Education and Adherence: Patient understanding of treatment options, adherence to prescribed therapies, and managing side effects are critical for successful outcomes. Educational efforts and support programs can enhance medication access and effectiveness.
Innovation and Access Balance: Balancing incentives for pharmaceutical innovation with ensuring affordable access to medicines remains a key challenge. Strategies such as public-private partnerships, alternative funding models, and incentivizing research in neglected areas aim to address this balance.