:
Biopharmaceuticals and Biotechnology: Biopharmaceuticals, which include biologics and biosimilars, are medications derived from biological sources such as proteins, antibodies, and nucleic acids. Understanding how these advanced therapies are developed, regulated, and used in treating complex diseases like cancer, autoimmune disorders, and rare genetic conditions can provide insights into the forefront of pharmaceutical innovation.
Drug Discovery and Development: Delving into the process of drug discovery—from initial research and preclinical studies to clinical trials and regulatory approval—can illuminate the challenges and breakthroughs in bringing new medications to market. This includes exploring the role of computational modeling, high-throughput screening, and molecular biology techniques in identifying potential drug candidates.
Health Technology Assessment (HTA): HTA evaluates the clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and broader societal impact of pharmaceuticals and other health technologies. Studying HTA methodologies and their application in decision-making by healthcare providers, insurers, and policymakers can reveal how pharmaceuticals are assessed for adoption into healthcare systems.
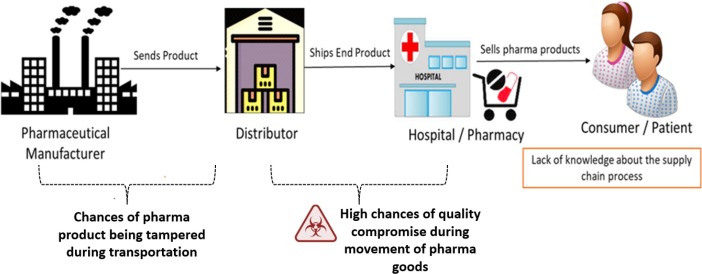
Pharmaceutical Supply Chain and Logistics: Examining the pharmaceutical supply chain—from manufacturing and distribution to storage and delivery—provides insights into ensuring drug availability, quality control, and minimizing supply disruptions. Topics may include cold chain logistics for biologics, supply chain resilience, and global distribution networks.
Regulatory Affairs and Pharmacovigilance: Regulatory affairs encompass the laws, regulations, and guidelines governing pharmaceutical development, marketing authorization, and post-market surveillance. Understanding pharmacovigilance processes for monitoring drug safety, adverse events reporting, and regulatory compliance is crucial for maintaining public trust and patient safety.
Healthcare Innovation Ecosystem: Exploring the collaborative efforts among pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, government agencies, and healthcare providers can showcase how innovation ecosystems foster research, development, and adoption of new therapies. This includes initiatives such as public-private partnerships, research consortia, and innovation hubs.
Healthcare Disparities and Access to Medications: Investigating disparities in access to pharmaceuticals across different demographics, geographic regions, and socioeconomic groups highlights challenges in achieving equitable healthcare. This includes studying initiatives to improve access, such as drug donation programs, differential pricing strategies, and policies to promote generic drug availability.
Digital Health and Telemedicine: The integration of digital technologies, including telemedicine platforms, mobile health apps, and electronic health records (EHRs), is transforming how pharmaceuticals are prescribed, monitored, and managed remotely. Exploring digital health innovations in medication adherence, patient education, and real-time health data analytics can illustrate their impact on healthcare delivery.
Healthcare Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Analyzing the environmental footprint of pharmaceutical production, waste management, and pharmaceutical residues in water systems underscores the importance of sustainable practices in healthcare. Topics may include green chemistry initiatives, eco-friendly packaging, and initiatives to minimize pharmaceutical waste.
Patient-Centered Care and Shared Decision-Making: Understanding how pharmaceuticals contribute to patient-centered care involves exploring initiatives that empower patients in treatment decisions, improve health literacy, and promote adherence to medication regimens. Topics may include patient support programs, shared decision-making tools, and the role of patient advocacy groups.
Clinical Trials and Drug Development: Understanding how pharmaceuticals go from concept to market through clinical trials can shed light on the rigorous process of testing safety, efficacy, and dosage in human populations. This process ensures that medications are safe and effective before they reach patients.
Health Economics and Policy: Exploring the economic impact of pharmaceuticals involves studying how drug pricing, access, and healthcare spending interplay at national and global levels. This includes examining healthcare policies that shape drug regulation, affordability, and reimbursement.
Precision Medicine and Pharmacogenomics: Learning about personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics can highlight how genetic information is used to tailor treatments to individual patients, improving therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse effects.
Global Health Challenges: Investigating how pharmaceuticals address global health challenges such as infectious diseases, antimicrobial resistance, and access disparities provides insight into the role of medications in improving health outcomes worldwide.
Ethical Issues in Healthcare: Delving into ethical considerations surrounding pharmaceuticals includes examining topics like patient consent in clinical trials, equitable access to medications, transparency in research, and the impact of industry practices on public health.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations: Exploring cutting-edge pharmaceutical research, including biotechnology, nanomedicine, and novel drug delivery systems, can showcase how innovation continues to drive improvements in healthcare outcomes.
Public Health Initiatives: Studying pharmaceutical contributions to public health initiatives, such as vaccination campaigns, disease eradication efforts, and health education programs, illustrates the broader impact of medications on population health.
Healthcare Systems and Infrastructure: Analyzing how pharmaceuticals interact with healthcare systems, including challenges related to distribution, supply chain management, and regulatory frameworks, provides a holistic view of their integration into healthcare delivery.
These topics offer a comprehensive view of how pharmaceuticals shape modern healthcare, addressing medical, economic, ethical, and global health dimensions. Exploring these areas can provide a deeper understanding of the opportunities and challenges associated with pharmaceutical innovation and its impact on patient care and public health outcomes.